John Proctor (1631-1692)
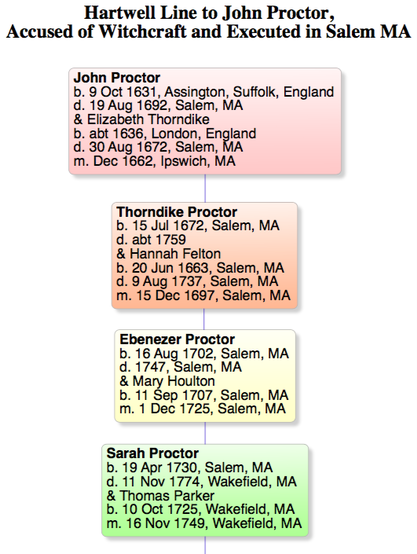
Click on the pedigree chart above to see it full size
John Proctor (9 Oct 1631 – 19 Aug 1692) was a farmer and tavern keeper in the Massachusetts Bay Colony. He was the son of John Proctor, Sr. (1594–1672) and Martha Harper (1607–1667). He died by hanging on August 19, 1692 in Salem Village, during the Salem Witch Trials after being accused and convicted of witchcraft.
Initial accusations were aimed at Proctor's third wife, Elizabeth (Bassett). When he began to defend her and vocally express his disbelief in the accusers, fingers were then pointed at him as well. Although Abigail Williams was John Proctor's chief accuser, he was also named by Mary Walcott, who stated he tried to choke her, and by his former servant Mary Warren on 21 April. Warren told magistrates that Proctor had beaten her for putting up a prayer bill before forcing her to touch the Devil's Book. Further allegations of an increasingly salacious nature followed. Proctor continued to challenge the veracity of spectral evidence and the validity of the Court of Oyer and Terminer, which led to a petition signed by 32 neighbors in his favor. The signatories stated that Proctor had lived a “Christian life in his family and was ever ready to help such as they stood in need”. The Proctors were tried on 5 August 1692, found guilty, and sentenced to death by hanging. While Proctor and his wife were still in jail, the sheriff seized all of their household belongings. The cattle were sold cheaply, slaughtered, or shipped to the West Indies. The beer barrels at the tavern were emptied. Their children were left with no means of support. Proctor was hanged on 19 August 1692. Elizabeth, who was then pregnant, was given a reprieve until she gave birth, which came after the trials ended.
Source: Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_Proctor_(Salem_witch_trials)
Initial accusations were aimed at Proctor's third wife, Elizabeth (Bassett). When he began to defend her and vocally express his disbelief in the accusers, fingers were then pointed at him as well. Although Abigail Williams was John Proctor's chief accuser, he was also named by Mary Walcott, who stated he tried to choke her, and by his former servant Mary Warren on 21 April. Warren told magistrates that Proctor had beaten her for putting up a prayer bill before forcing her to touch the Devil's Book. Further allegations of an increasingly salacious nature followed. Proctor continued to challenge the veracity of spectral evidence and the validity of the Court of Oyer and Terminer, which led to a petition signed by 32 neighbors in his favor. The signatories stated that Proctor had lived a “Christian life in his family and was ever ready to help such as they stood in need”. The Proctors were tried on 5 August 1692, found guilty, and sentenced to death by hanging. While Proctor and his wife were still in jail, the sheriff seized all of their household belongings. The cattle were sold cheaply, slaughtered, or shipped to the West Indies. The beer barrels at the tavern were emptied. Their children were left with no means of support. Proctor was hanged on 19 August 1692. Elizabeth, who was then pregnant, was given a reprieve until she gave birth, which came after the trials ended.
Source: Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_Proctor_(Salem_witch_trials)
Additional Sources
John Proctor, from Professor Douglas O. Linder's Famous Trials website
John Proctor entry on Find-A-Grave
John Proctor: First Male Accused Witch of the Salem Witch Trials, from the History of Massachusetts blog
John Proctor, from Professor Douglas O. Linder's Famous Trials website
John Proctor entry on Find-A-Grave
John Proctor: First Male Accused Witch of the Salem Witch Trials, from the History of Massachusetts blog